作者:Qingyuan Qin 1 Qingdan Shi 1 Wen Sun 1·Junmin Wan 1, 2·Zhiwen Hu1
来源:Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics
DOI:10.1007/s10854-018-8883-9
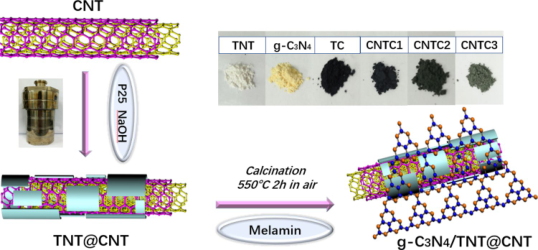
摘要:The purpose of this research is to design and fabricate a novel ternary hybrid nanostructure heterojunction with high-efficiency visible-light-driven photocatalysis. The porous layered TiO2 nanotubular structures (TNTs) with high percentage of photocatalytic reactive facets, which were turned into by commercially available TiO2, were wrapped on the surface of hydroxylation carbon nanotubes (CNTs) through the formation of Ti–O=C and/or Ti–O–C bond between CNTs and TiO2. Then the TNT@CNT nanotubular composites were coated by ultrathin g-C3N4 nanosheets with a thickness of 3–4 nm. The ternary nanocomposites owned strong absorption performance, low charge recombination rates and high-efficiency photocatalytic activities, which were all owe to high surface areas and excellent adsorptivity of the CNTs, photocatalytic performance of TiO2 nanotubes (TNTs) and moderate band gap of g-C3N4 nanosheet. What’s more, the formation of chemical bonds greatly improved visible-light photocatalytic activity with a degradation rate of 98.2 and 97.9% for methylene blue and rhodamine B in 60 min under visible-light irradiation, which showed ~ 10 times enhancement compared to pure TiO2. In addition, the existence of h + and ·OH and ·O2− radicals played main role in the photocatalytic process. The new material was of great significance to environmental protection and energy criss.
插图: